Stem Cell Therapy for Heart Disease
Innovations Stem Cell Center was named the #1 Stem Cell Clinic in the USA by Life Sciences Review Magazine.
Heart disease comes in many forms. Peripheral vascular disease shares the same primary cause as the most common form of heart disease – atherosclerosis. This article will cover the following:
Q: What kinds of heart disease can stem cells potentially help?
A: As mentioned above, heart disease can come in many forms. The most common is atherosclerosis, which is known as coronary artery disease (CAD) when the heart is involved. In CAD cholesterols builds up in the arteries that supply oxygen to the muscle of the heart. When enough cholesterol builds up, the artery can be blocked and cause the muscle to die. When that happens it is called a myocardial infarction (MI) or a heart attack. Heart attacks damage the heart muscle. This can result in numerous problems including arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats and heart failure. The blockage can be treated with stents and bypass surgery. Medications are also used to limit new cholesterol formation. Unfortunately, when enough heart damage has occurred, heart failure may result despite stents or surgery.
Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle is unable to perform its pumping job. Blood tends to back up, especially in the lungs leading to shortness of breath. Other causes of heart failure besides CAD include cardiomyopathy, heart valve disease and poorly controlled hypertension. The most common treatment for heart failure is medications. The average heart failure patient is on 11 medications for their conditions. Heart failure is the most common form of heart disease for which stem cells have been used. Stem cells have been used for heart failure after heart attacks and for cardiomyopathy. We do not yet have the ability for stem cells to fix heart valves themselves. However, stem cells may be effective for heart failure that results from heart valve issues.
Stem cells may also be effective for some heart arrhythmias. Only limited numbers of patients have received treatment for arrhythmias, so meaningful statistics are unavailable. This is a promising area since most people that die from heart disease die from an arrhythmia, so improving the efficacy of treatments is very important.
Q: What is an adult stem cell?
A: All stem cells, adult stem cells or from other sources share two important characteristics:
1. The ability to multiply. This means in theory they can make an infinite number of copies.
2. The ability to become any type of cell. For example, stem cells from fat can become skin, muscle, or bone stem cells. The transformed cell can then make an infinite number of copies. For more information read our blogs What are Stem Cells and Understanding Adipose-Derived Stem Cells.
Stem cells that are obtained from mature adult tissues are referred to as adult stem cells. The potential exists for adult stem cells to become any type of cell. This ability to become any type of cell and then make as many cells as needed make adult stem cells an area of extreme interest. Some adult stem cells also have widespread availability. We simply have to harvest them from adult tissues. The two tissues most commonly used tissues to obtain or harvest adult stem cells are bone marrow and fat.
Fat adult stem cells are also known as adipose-derived adult stem cells. See our blog Understanding Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Adult stem cells from fat are easier to obtain and exist in larger numbers than bone marrow adult stem cells. These qualities have resulted in an increasing interest in fat (adipose) derived adult stem cells. For more information on stem cells visit:
https://stemcellrevolution.com/
Q: How are adult stem cells harvested from fat?
A: Harvesting adult stem cells from fat is a simple process. Many heart failure and PVD patients are on anti-coagulants or “blood thinners”. When allowed by your doctor or cardiologist we prefer stopping blood thinners for a few days before and after harvesting. However, if your doctors feels it is unwise to stop the blood thinner, we can do the harvest while on them. We begin by selecting an area to take the fat like the stomach or leg. We sterilize the area using a local anesthetic solution that is injected into the area. Using a syringe and a tool called a cannula, we suction out a 50 ml (about 1 1.2 oz.) of fat.
Some patients experience some swelling and /or bruising after the harvesting procedure. Typically this resolves in 2-3 weeks. We do give a prescription for pain medications in case you need them. Using ice on the harvest area for a few days post operatively can reduce the swelling and bruising.
Next we take the fat and use a centrifuge and incubator to do some simple processing to isolate the adult stem cells. The final product is called Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF). SVF is a very powerful mixture. SVF contains a large numbers of adult stem cells, up to about 100 million of them. SVF also contains a large amount of growth factors. Growth factors are the chemical messengers our cells use to talk to each other. Growth factors have been referred to as text messages between cells. The growth factors harvested in SVF tend to be highly anti-inflammatory. We are now ready to deploy the SVF for your osteoarthritis. We can also use it for many other disorders. Numerous deployment protocols under investigation for a large number of disorders.
Q: How are adult stem cells deployed for heart failure?
A: After harvest and processing, stem cells are given IV for heart failure. The stem cells are attracted to areas of injury or inflammation, so this helps them find the correct area to help the heart. In other countries, stem cells are being injected directly into the heart muscle for heart failure. We are not currently doing injections into the heart in our network.
Q: How are adult stem cells deployed for peripheral vascular disease?
A: Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) also receives the stem cells IV after harvest and processing. In addition, stem cells are injected into the healthier tissue near an ulcer or extremity experiencing blood flow problems.
Q: What results can I expect from adult stem cells heart failure?
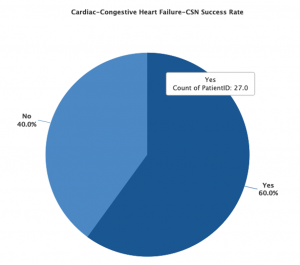
A: Our network gathers statistics from patients all across the country to follow how patients respond to stem cells. In mid- 2019 about 60% of heart failure patients have seen improvement with IV stem cell therapy.
As more patients are treated we will be able to determine which type of heart failure responds best and how to improve the treatment.
Q: What results can I expect from adult stem cells for peripheral vascular disease?
A: Peripheral vascular disease, especially small vessel disease responds well to stem cells. Many patients have seen ulcers and wounds heal that had not been healing before stem cell therapy. Some patients have been able to avoid amputation using stem cells.
Q: How do I get started using my own stem cells for heart and/or vascular disease?
Cost of Stem Cell Treatments
$12,500 for initial treatment
Your investment includes:
✅ Complete medical evaluation
✅ Stem cell harvest & processing
✅ IV stem cell deployment
✅ Follow-up care included
Second treatment (if needed): $5,000
Financing up to 60 months available.
A: Getting started is easy. You can click on the Schedule a Consult button on this page or you can call:
Dallas Practice Location: 214-643-8665
And schedule a consult with one of our trained consultants.
Our adipose-derived stem cells yield 100 million cells per treatment – compared to just 100,000 from bone marrow.