Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States. It is also a leading cause of chronic disability in the United States. Unfortunately, treatment for stroke remains limited. Stem cells are showing some real promise for patients who have suffered a stroke.
What is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood flow is cut off to part of the brain. When that occurs, the brain tissue that loses its blood supply is injured or killed. This results in a loss of function in the body based on what the damaged area of the brain controls. For example, if the area controlling movement of the left arm is damaged, that arm will become weak or paralyzed. If the area controlling sensation on the left arm is also involved, the arm will be numb or may have burning or pain sensations as well. Since the brain controls all of our movement and sensations, including sight and speech, almost anything can be impacted by a stroke.
What Are the Types of Stroke?
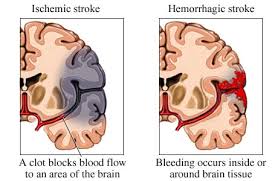
In general, there are two types of stroke, ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes are the most common. Ischemic strokes occur when the blood vessel to part of the brain is blocked, typically by a blood clot or a build-up of cholesterol similar to a heart attack.
Hemorrhagic strokes are the less common form of stroke. They occur when a blood vessel leaks and there is bleeding into and around the brain. Knowing which type of stroke is present is essential in the early treatment of stroke.
What Can be Done to Treat a Stroke?
Stroke treatment has improved only slowly. If treated in the first few minutes, the damage from an ischemic stroke can be reversed or limited using special drugs (alteplase or tissue plasminogen activator) in an Emergency Room or hospital. This drug can break up the clot blocking the blood vessel. If used in the first few minutes to hours, it can avoid or limit any damage to the brain. It is essential that CT imaging is done to determine the type of stroke to confirm it is not hemorrhagic prior to using alteplase. Since alteplase breaks up a clot, it can cause severe worsening or death if used with a hemorrhagic stroke. Hemorrhagic strokes are sometimes treated to avoid further hemorrhage.
After the first few hours, there is no specific treatment for strokes. Ischemic stroke patients are often treated with anticoagulants (blood thinners) in hopes of preventing more clots. Most of the treatment is rehabilitation to try to improve function after the stroke. Recovery, if any, occurs gradually over several months to a year or more.
What Can Stem Cells Do for a Stroke?
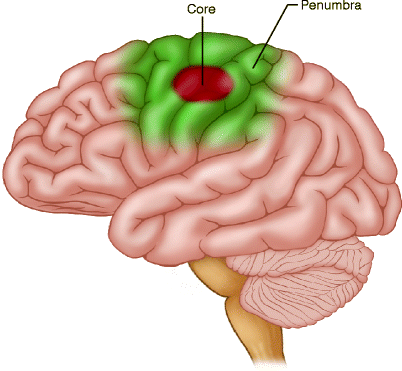
Stem cells have been shown to help in stroke patients. They can help in several ways. The first way they can help is by reducing inflammation around a stroke. In most strokes, there is a “core” area where the brain cells have died surrounded by an area of damage called the “penumbra”.
The brain cells in the penumbra usually do not work well because they are damaged, but they are still alive. Stem cells can help cells in the stroke area in several ways: See our blog What are Stem Cells?
Ways Stem Cells Can Help Brain Cells in a Stroke
- Stem cells can reduce inflammation in the penumbra zone, helping the cells recover
- Stem cells are very good at encouraging new blood vessels. This can help restore blood flow to the cells in the penumbra zone.
- Stem cells produce new cells in the penumbra zone
- Stem cells may be able to produce new blood vessels and brain cells in the core zone.
This makes stem cell therapy the first treatment to show promise in actually restoring brain cell function after a stroke.
How Well Do Stem Cells Work for a Stroke?
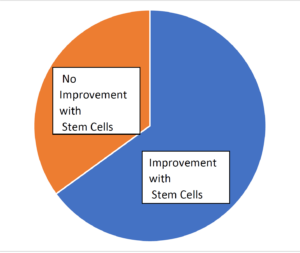
The results of stem cells for stroke have been encouraging. The Cell Surgical Network has treated over 170 stroke patients and more than 65% have seen improvement.
Results From the First 170 Stroke Patients Treated with Stem Cells by Cell Surgical Network
This has been done by giving the patients the stem cells via an IV. Usually, a drug called mannitol is given prior to the cells to help the stem cells get into the brain tissue. The majority of patients have received a single treatment, but several have seen additional improvement with more stem cell therapy. The exact number of cells and treatments that are best is still being determined.
Cost of Stem Cell Treatments
The cost of the initial treatment procedure ranges from $5,000 to $10,000. The range in cost is dependent on the complexity of delivering the cells back to you. For example, spine conditions require multiple physicians to deliver the cells back to your body and this requires an increase in cost as multiple doctors are involved in the procedure. For many people the initial treatment is all that is needed; however, for some conditions, subsequent treatments may be required and these are done at a reduced fee. Innovations Medical offers stem cell treatment procedures at our Dallas practice location.
Read More on Our Blog Understanding Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Call our office to schedule a consultation to learn more.